Property Derivations
Property Derivation scripts allow properties to be derived whenever a new member is being created, or properties of an existing member are being updated.
Property Derivations execute when:
- A new member is created
- An existing member's properties are modified
- Properties need automatic calculation
These scripts are associated in the Property -> Derivations screen as shown below.
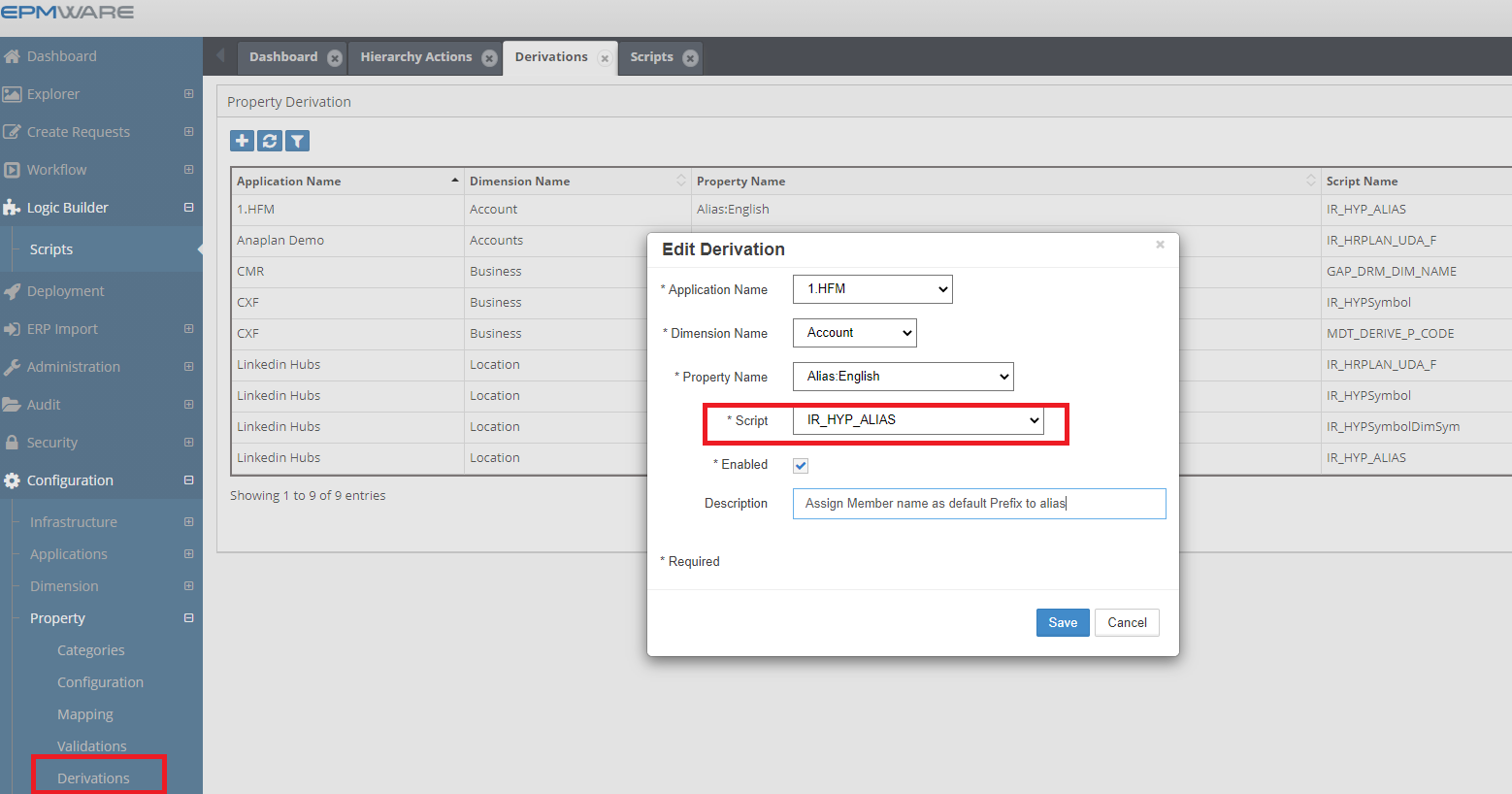
Figure: Property Derivations Script Association