Creating Logic Builder Scripts
This guide walks through the process of creating new Logic Scripts in EPMware, from initial creation to testing and deployment.
Accessing Logic Builder
Navigate to the Logic Builder module through the Configuration menu:
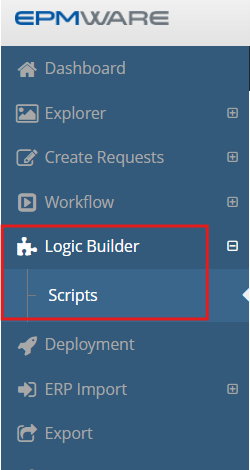
Figure: Accessing Logic Builder from the Configuration menu
📝 Creating a New Script
Step 1: Open New Script Dialog
Click the plus sign (➕) in the Scripts menu to create a new Logic Script:
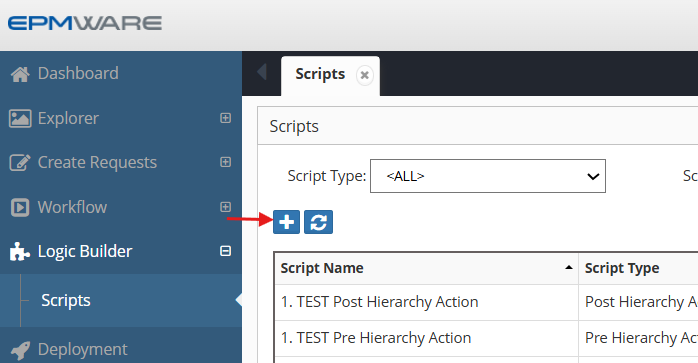
Figure: Plus icon for creating new scripts
Step 2: Configure Script Properties
Enter the following information in the script creation dialog:
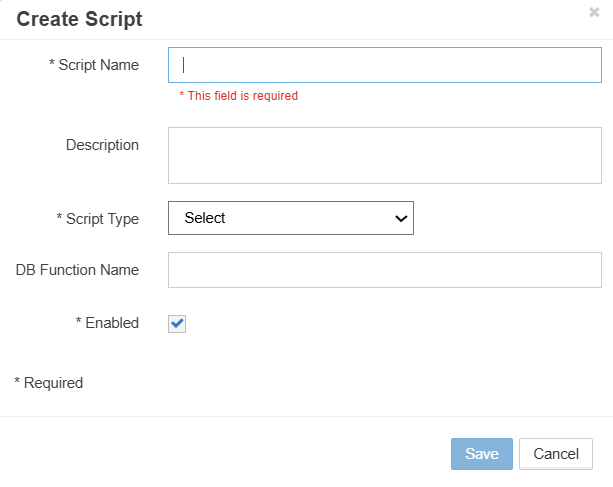
Figure: New Script configuration dialog
-
Script Name (Required)
- Enter the name of the script.
- Must be unique across all script types and can be up to 50 characters long.
- All EPMware out of the box Logic Scripts will have a prefix of “EW_”. Please use a common prefix for all your custom Logic Scripts.
-
Description (Optional)
- Provide meaningful description of script purpose
-
Script Type (Required)
- Select from dropdown list
- Determines when and how the script executes
- Cannot be changed after creation
-
DB Function Name (Optional)
- Reference to stored Oracle Procedure name OR stored packaged procedure
- If this field is populated, then the Script Editor gets disabled for this record
- This option is available for On Prem Customers only. For All Cloud customers this option should not be used
-
Enabled
- This checkbox enables or disables this script.
- If the script is disabled, then it will not be executed.
🧪 Script Editor Interface
Once the script is created, the Script Editor opens:
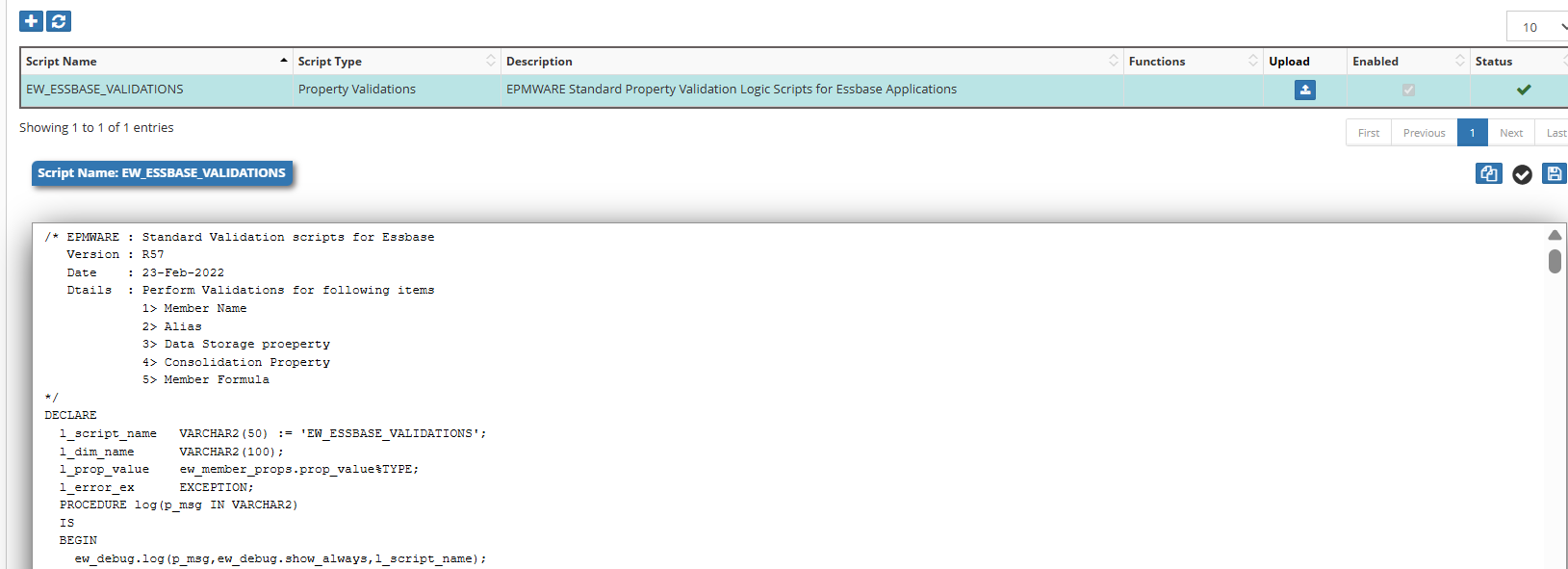
Figure: Logic Builder Script Editor with syntax highlighting